

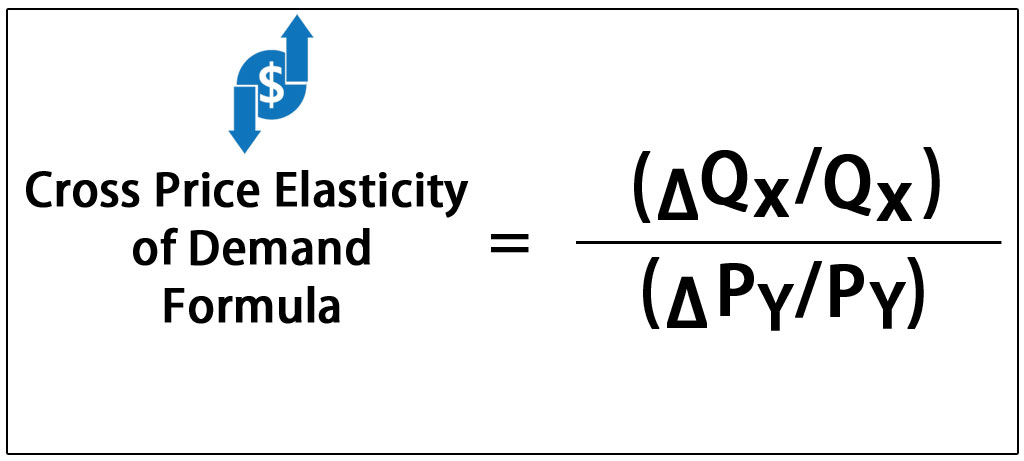
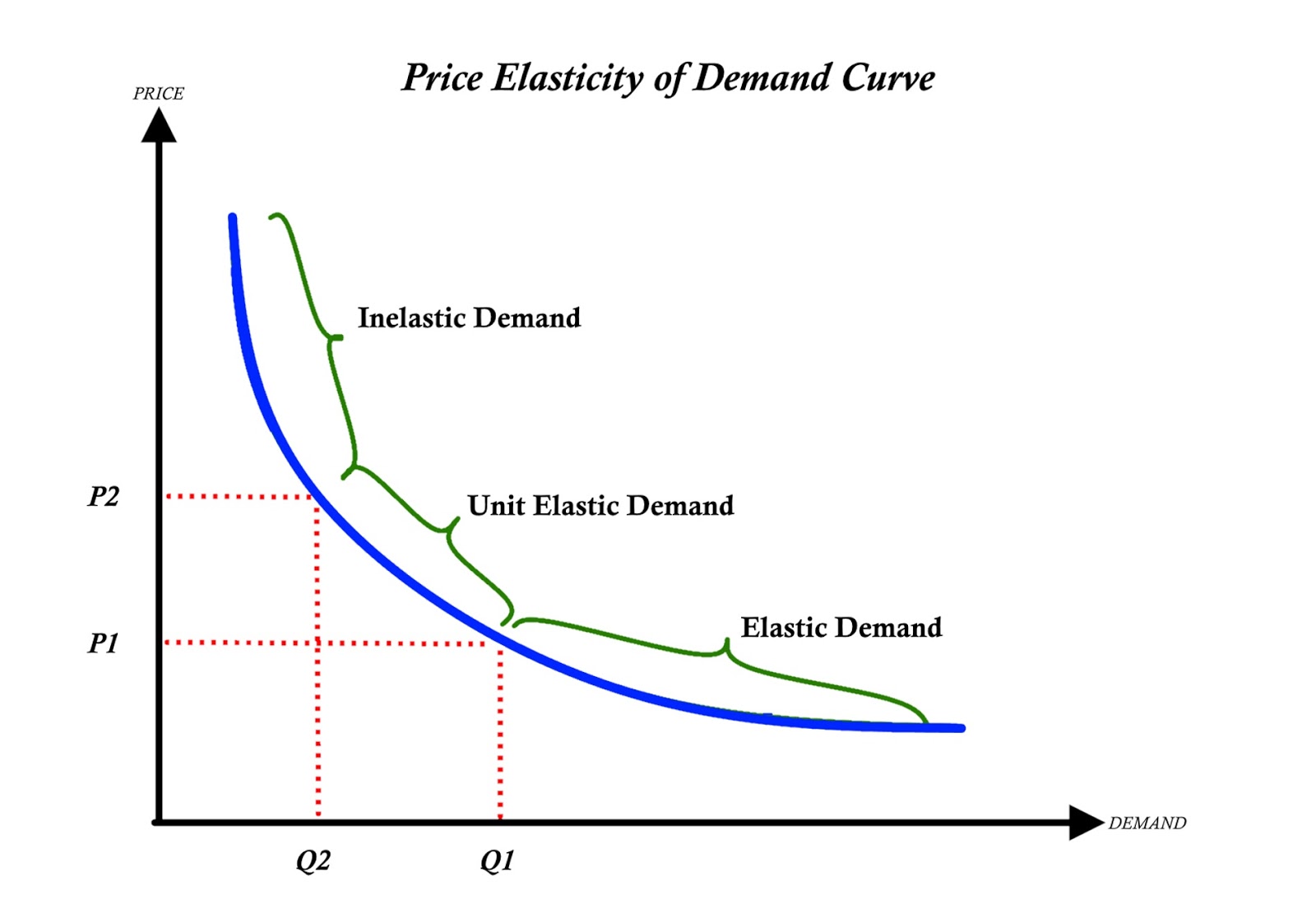
If the absolute value of the elasticity of demand is less than one, just like the example we just gave for oil, we say that the demand curve is inelastic. So we often drop the negative sign and write that the elasticity of demand is 0.5. When price goes down, the quantity demanded goes up. Elasticities of demand are always negative because when price goes up, the quantity demanded goes down. So the elasticity of demand is -5% divided by 10%, or -0.5. That's -5% divided by the percentage change in the price. So, if the price of oil increases by 10% and over a period of several years the quantity demanded falls by 5%, then the long run elasticity of demand for oil is what? Well, elasticity is the percentage change and the quantity demanded. Delta is the symbol for change in, so this is the percentage change in the quantity demanded divided by the percentage change in the price. The elasticity of demand is equal to the percentage "change in". The elasticity of demand is the percentage change in quantity demanded divided by the percentage change in price. So here's a more precise definition of elasticity. How to calculate with some data on prices and quantities, what the elasticity is over a range of the demand curve. In this lecture, we're going to show how to create a numeric measure of elasticity. It measures the responsiveness of the quantity demanded to a change in price. In our first lecture on the elasticity of demand, we explain the intuitive meaning of elasticity.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
